Your cart is currently empty!
Introduction
In today’s cloud-first and SD-WAN-driven enterprise networks, choosing the right router is critical for performance, security, and scalability. The Cisco Catalyst 8000 Series routers—including the Catalyst 8200, 8300, and 8500—represent Cisco’s new generation of edge routing platforms designed to deliver secure connectivity from branch to cloud.
This guide provides a complete Catalyst 8000 series router comparison, explaining the strengths of each sub-series and offering a step-by-step selection guide for your deployment. Whether you’re evaluating Catalyst 8200 vs 8300 vs 8500, planning a WAN refresh, or migrating from ISR 4000 routers, this article will help you make an informed and future-proof decision.
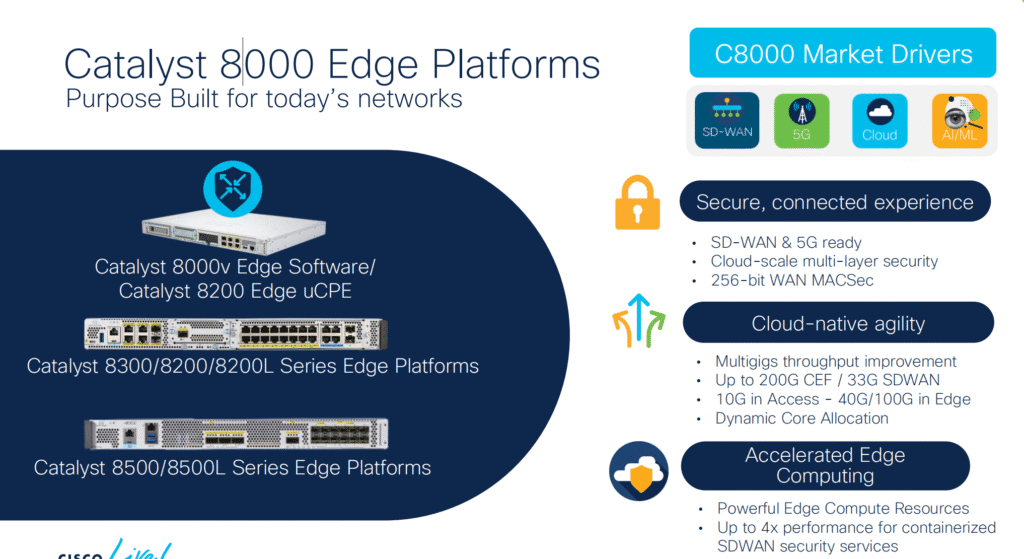
Catalyst 8000 Series Overview
The Cisco 8000 Series Edge Platform family integrates high-performance routing, SD-WAN, cloud on-ramp, and advanced security in a unified system. Built on modern Cisco Silicon One architecture, it provides cloud-scale agility and hardware acceleration for encrypted traffic.
Key advantages include:
- High throughput and scalability supporting 1G to 100G interfaces for future traffic growth.
- Integrated SD-WAN and SASE features to simplify branch connectivity.
- Programmable and API-driven IOS XE software, enabling automation and telemetry.
- Flexible deployment options covering small, medium, and large edge scenarios.
The family is structured into three major tiers: Catalyst 8200, Catalyst 8300, and Catalyst 8500—each optimized for different performance levels and branch types.
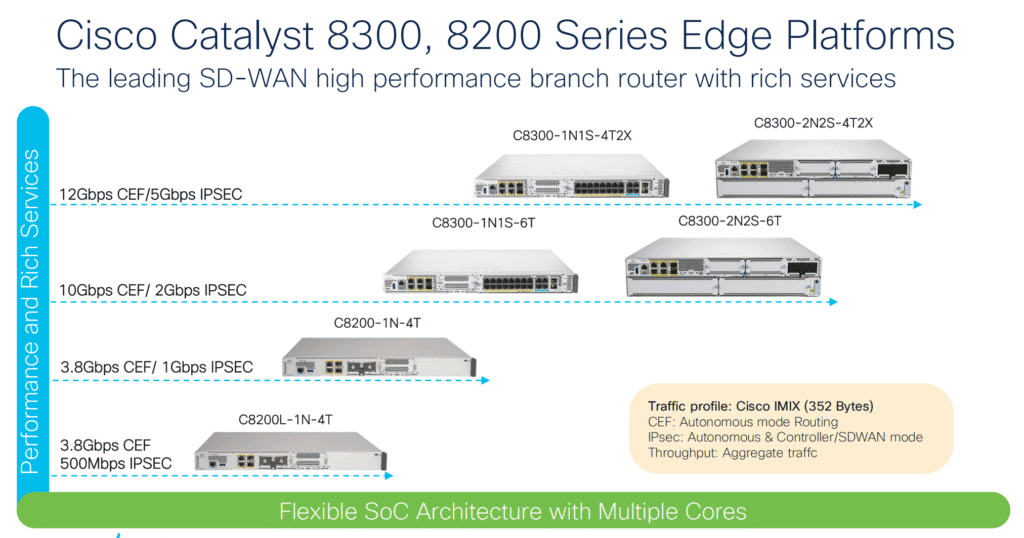
Catalyst 8200 Series – Small Branch Edge
The Catalyst 8200 Series is designed for small branch networks that require secure connectivity, SD-WAN services, and reliable performance in a compact form factor.
- Up to around 3.8 Gbps CEF throughput and 1 Gbps IPSec performance depending on model.
- Typically 1 RU fixed platforms with RJ-45 and SFP WAN ports.
- Excellent price-performance ratio for smaller offices or edge sites.
- Ideal for organizations seeking to replace ISR 4300 routers with modern SD-WAN capabilities.
Best for: Small enterprises and branches with moderate traffic demands and limited WAN links.
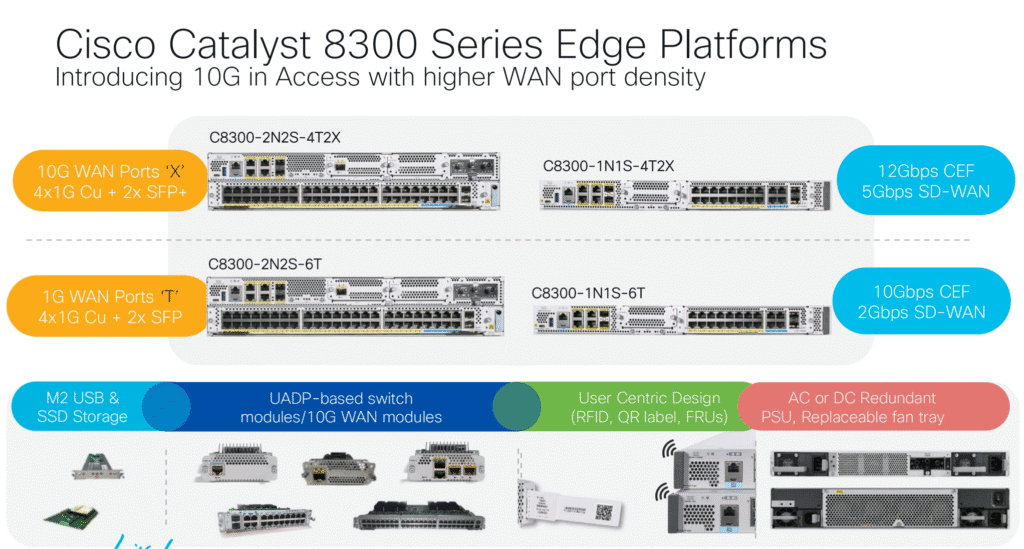
Catalyst 8300 Series – Mid-Size Branch or Cloud Edge
The Catalyst 8300 Series serves as the versatile mid-tier in the family, bridging the gap between compact 8200 routers and the high-end 8500 models.
- Supports up to 12 Gbps CEF throughput and 5 Gbps IPSec performance.
- Modular design with NIM/SM slots for expansion of WAN, LAN, LTE, and 5G interfaces.
- Dual redundant power supplies and advanced cooling for mission-critical uptime.
- Rich integration with SD-WAN controllers and cloud security services (Cisco Umbrella, SIG Gateway).
Best for: Medium-sized enterprises or cloud edge deployments needing flexibility and future scalability.
Catalyst 8500 Series – High-Performance Aggregation Edge
At the top of the Catalyst 8000 family, the Catalyst 8500 Series targets high-performance sites, aggregation layers, and data center edges.
- Offers 100G interfaces and hardware-accelerated encryption for heavy traffic environments.
- Engineered for multi-gigabit SD-WAN, SASE, and cloud aggregation deployments.
- Combines high port density with advanced security and telemetry.
Best for: Large enterprise hubs, service providers, and organizations requiring maximum throughput and scalability.
Catalyst 8200 vs 8300 vs 8500 – Feature Comparison
|
Series |
Performance |
Interface Flexibility |
Ideal Use Case |
Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Catalyst 8200 |
Up to 3.8 Gbps CEF / 1 Gbps IPSec |
4× WAN ports (2× RJ45 + 2× SFP) |
Small branch edge |
Cost-efficient, compact SD-WAN router |
|
Catalyst 8300 |
Up to 12 Gbps CEF / 5 Gbps IPSec |
Modular NIM/SM slots, PoE, 10G uplinks |
Mid-size branch or cloud edge |
Expandable, flexible, rich services |
|
Catalyst 8500 |
40G / 100G support, multi-gig IPSec |
High-density 100G ports |
Aggregation edge / data center |
Maximum scalability and encryption performance |
This table provides a concise view of the Catalyst 8200 vs 8300 vs 8500 differences — essential for anyone comparing Cisco’s latest WAN-edge offerings.
How to Choose the Right Cisco 8000 Series Router
When evaluating the Cisco Catalyst 8000 Series, consider the following factors to match your use case:
- raffic and performance requirements
Estimate your current and future WAN throughput. If your average site runs below 1 Gbps, the 8200 is ideal. For multi-link SD-WAN sites, the 8300 offers headroom; for high-density hubs, choose the 8500. - Interface and module needs
The 8300’s modular slots enable greater customization (5G, switch modules, PoE). The 8200 is simpler but fixed. The 8500 is designed for aggregation with 10/40/100G ports. - Security and SD-WAN services
All Catalyst 8000 routers run Cisco IOS XE with built-in SD-WAN capabilities. Models can integrate Umbrella, DIA, and SASE for end-to-end security. - Licensing and subscription tiers
Cisco DNA Essentials and DNA Advantage licenses define feature sets and controller management terms (3/5/7 years). Always factor license cost into TCO. - Deployment scale and growth
If you plan to expand over 3–5 years, select a model with room for throughput and port growth rather than the bare minimum.
Quick Recommendations
- For small branches with modest bandwidth needs → Catalyst 8200 Series
- For medium branches and cloud edge deployments → Catalyst 8300 Series
- For large enterprises, aggregation, and data center edge → Catalyst 8500 Series
Each series uses the same IOS XE code base and supports controller management via Cisco DNA Center or vManage, so transitioning between models is simple as you scale.
Conclusion
Selecting the right Catalyst 8000 series router is not just about raw performance numbers—it is about fit, scalability, and cost efficiency. The Catalyst 8200 offers an entry-level path for smaller branches, the 8300 delivers versatility and growth, and the 8500 provides the horsepower for aggregation and large-scale SD-WAN deployments.
When planning your upgrade or migration from ISR 4000 routers, analyze your network traffic, link diversity, and future cloud strategy. By aligning these factors with the Catalyst 8200 vs 8300 vs 8500 differences, you can achieve an optimized, secure, and future-ready WAN architecture.
FAQ
Q1: What are the key differences between the Catalyst 8200, 8300 and 8500 Series?
The 8200 Series targets small-branch sites with moderate throughput; the 8300 Series suits mid-size branches and cloud-edge with higher performance and modularity; the 8500 Series is designed for high-performance hubs/aggregation with very high throughput and dense interfaces.
Q2: Is a software subscription license mandatory for the Catalyst 8000 Series routers?
Yes — a Cisco DNA subscription is required at the time of purchase to enable features and full operation of the Catalyst 8000 family.
Q3: Can I choose a lower-tier model (e.g., 8200) now and upgrade later?
You can, but you should evaluate future growth (traffic, interfaces, services). If you anticipate significant scaling, selecting the mid or high tier (8300 or 8500) upfront may reduce cost and disruption later.
Q4: Do the Catalyst 8000 Series support SD-WAN, cloud-edge and high-speed interfaces?
Yes — all series support SD-WAN and modern edge services. The 8300 and 8500 offer higher interface speeds (10 G/25 G/100 G) and advanced modules for cloud-edge deployments.
Q5: What should I check when choosing the right model?
Look at your current and expected traffic volume, interface/link requirements (WAN, LAN, 10/25/100 G), type of services (security, SD-WAN), budget (hardware + software/licensing + operations) and future growth headroom. Matching these to the right series (8200/8300/8500) ensures a proper fit.
