Your cart is currently empty!
Cisco’s Integrated Services Router (ISR) 4000 Series has reached its End of Life (EoL) and End of Support (EoS) milestones, prompting many enterprises to plan their next-generation WAN and SD-WAN strategies. The logical successor is the Cisco Catalyst 8000 Series (C8200, C8300, C8500, and C8500L) — built on a modern IOS XE architecture and a unified DNA licensing framework.
This article explains why ISR4000 is being retired, how Catalyst 8000 replaces it, and what to consider when migrating, especially around DNA licensing and bandwidth tiers.
Cisco ISR4000 EoL and EoS Overview: Key Dates and Impact
Cisco has announced End-of-Life (EoL) and End-of-Support (EoS) dates for the ISR 4000 family, including:
|
Model |
End of Sale |
End of SW Maintenance |
End of Support (EoS) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ISR 4221 |
Aug 2024 |
Aug 2026 |
Aug 2029 |
|
ISR 4321 / 4331 |
Jul 2024 |
Jul 2026 |
Jul 2029 |
|
ISR 4351 / 4431 / 4451 |
Jul 2024 |
Jul 2026 |
Jul 2029 |
While existing routers will continue to function, Cisco has ceased new feature development and stopped offering hardware refreshes. The Catalyst 8000 family is now the strategic replacement for all ISR 4000 deployments.
In short: ISR4000 is stable but frozen. Catalyst 8000 is the platform that will continue evolving under Cisco’s DNA architecture.
Why You Should Replace Cisco ISR4000 with Catalyst 8000 Routers
The move is not just a lifecycle refresh — it’s a foundation shift for the next decade of WAN connectivity.
Key reasons to upgrade:
- Lifecycle: ISR 4000 is in EoL/EoS phase — no future updates or hardware refresh options.
- Performance: C8000 delivers 2–5× higher IMIX throughput, up to 90Gbps aggregate, and supports modern encryption (AES-GCM).
- Licensing: Simplified DNA subscription model (Network Stack + DNA Stack) replaces the legacy perpetual SKU maze.
- Security & SD-WAN: Native Cisco SD-WAN (vManage) and Zero-Trust segmentation.
- Investment Protection: DNA licenses can migrate from ISR/ASR to C8000 under Cisco’s Smart Licensing system.
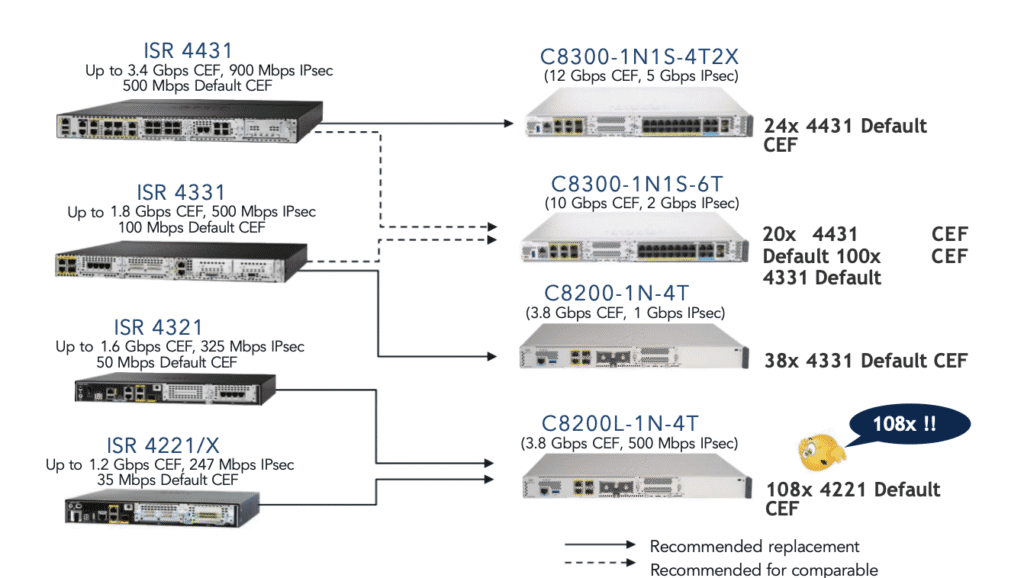
Model Replacement Chart: ISR4221, ISR4331, ISR4451 → C8200, C8300, C8500
Performance Comparison and Feature Parity
Below is a field-tested migration mapping based on performance equivalence and feature parity.
|
Legacy ISR 4000 |
Typical Performance |
Recommended Replacement |
New Performance |
Recommended DNA Tier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ISR 4221 |
~1.2 Gbps / 250 Mbps encrypted |
C8200-1N-4T or C8200L-1N-4T |
~3.8 Gbps / 0.5–1 Gbps |
DNA Essentials (T0–T1) |
|
ISR 4321 |
~1.6 Gbps / 325 Mbps encrypted |
C8200-1N-4T |
~3.8 Gbps / ~1 Gbps |
DNA Advantage (T1) |
|
ISR 4331 |
~1.8 Gbps / 500 Mbps encrypted |
C8300-1N1S-6T |
~10 Gbps / ~2 Gbps |
DNA Advantage (T2) |
|
ISR 4351 |
~3.4 Gbps / 900 Mbps encrypted |
C8300-2N2S-6T |
~10 Gbps / ~2 Gbps |
DNA Advantage (T2) |
|
ISR 4431 / 4451 |
~3.8 Gbps / 1.6 Gbps encrypted |
C8300-2N2S-4T2X |
~12 Gbps / 5 Gbps |
DNA Advantage (T2–T3) |
Choosing the Right Model Based on Site Size
If your ISR 4000 was already running near its maximum utilization, choose a Catalyst 8000 model two tiers higher to ensure headroom for future SD-WAN, telemetry, or cloud security services.
Cisco ISR4400 vs C8300 Product Comparison
|
Specification |
C8300-2N2S-4T2X |
ISR4451 |
C8300-1N1S-6T |
ISR4431 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
IPsec Tunnels |
6000 |
4000 |
6000 |
3500 |
|
SD-WAN IPsec |
5 Gbps |
1 / 1.4 Gbps (**) |
1.8 Gbps |
490 / 750 Mbps (**) |
|
CEF (Routing) |
12+ Gbps |
1 / 3.8 Gbps (**) |
10+ Gbps |
0.5 / 3.4 Gbps (**) |
|
Non-SD-WAN IPsec |
5 Gbps |
1 / 1.8 Gbps (**) |
1.9 Gbps |
0.5 / 1 Gbps (**) |
|
DRAM |
Default 8 GB / Up to 32 GB |
Default 4 GB / Up to 16 GB |
Default 8 GB / Up to 32 GB |
Default 4 GB / Up to 16 GB |
|
Embedded Ports / Modularity |
4 × RJ45 + 2 × SFP+ / 2 × NIM + 2 × SM + 1 × PIM |
4 × RJ45/SFP / 3 × NIM + 2 × SM |
4 × RJ45 + 2 × SFP+ / 1 × NIM + 1 × SM + 1 × PIM |
4 × RJ45/SFP / 3 × NIM |
Cisco ISR4300 vs C8200 Product Comparison
|
Specification |
C8200-1N-4T |
ISR4331 |
C8200L-1N-4T |
ISR4321 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
IPsec Tunnels |
2500 (SD-WAN) |
1000 (SD-WAN) |
1500 (SD-WAN) |
250 (SD-WAN) |
|
SD-WAN Performance |
1 Gbps |
100 Mbps* / 485 Mbps** |
500 Mbps |
50 Mbps* / 300 Mbps** |
|
CEF (Routing) |
3.8 Gbps |
100 Mbps* / 1.8 Gbps** |
3.8 Gbps |
50 Mbps* / 1.6 Gbps** |
|
IPSec (Non-SD-WAN) |
1 Gbps |
100 Mbps* / 445 Mbps** |
500 Mbps |
50 Mbps* / 300 Mbps** |
|
DRAM |
Default 8 GB / Up to 32 GB |
Default 4 GB / Up to 16 GB |
Default 4 GB / Up to 32 GB |
Default 4 GB / Up to 8 GB |
|
Embedded Ports / Modularity |
2 × RJ45 + 2 × SFP / 1 × NIM + 1 × PIM |
2 × RJ45 + 1 × RJ45/SFP / 2 × NIM + 1 × SM |
2 × RJ45 + 2 × SFP / 1 × NIM + 1 × PIM |
1 × RJ45 + 1 × RJ45/SFP / 2 × NIM |
Understanding Cisco DNA Licensing for Catalyst 8000 Migration
Network Stack (Perpetual License)
Provides baseline routing (IOS XE, DMVPN, GETVPN, FlexVPN, etc.) and never expires — routing continues even after DNA subscription ends.
DNA Stack (Subscription License and Terms)
Time-limited (3/5/7 years) and enables SD-WAN control, DNA Center automation, and analytics. Required for controller mode.
DNA Essentials vs DNA Advantage Explained
|
License Type |
Duration |
Controller Support |
Renewal Needed |
Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
DNA Essentials |
3Y/5Y |
Limited |
Optional |
Traditional routing |
|
DNA Advantage |
3Y/5Y/7Y |
Full (vManage/DNAC) |
Required |
SD-WAN & analytics |
Step-by-Step Migration Plan from ISR4000 to Catalyst 8000
1. Assessment and Planning Phase
- Inventory ISR hardware, throughput, and VPN utilization
- Gather license entitlements from Smart Account
- Estimate future encrypted traffic growth
2. Design and Licensing Phase
- Map each ISR to Catalyst 8000 equivalent
- Choose DNA subscription (3/5/7Y) and BW tier
- Plan for HSEC activation
3. Implementation and Rollout
- Pilot with one site under Autonomous Mode
- Validate routing, QoS, NAT, and SD-WAN template behavior
- Migrate site by site with rollback configuration retained
Related Reading: DNA Licensing, Bandwidth Tiers, and SD-WAN Migration
FAQ
Q1. What does Cisco ISR4000 EoL mean for existing users?
Cisco has announced End-of-Life (EoL) and End-of-Support (EoS) for ISR4000 routers, meaning no new software updates or hardware refresh options will be provided. Users should plan migration to the Catalyst 8000 series.
Q2. Which Catalyst 8000 model replaces Cisco ISR4331 or ISR4351?
Cisco recommends the Catalyst C8300-1N1S-6T or C8300-2N2S-6T as direct replacements for ISR4331 and ISR4351, offering higher throughput, SD-WAN support, and flexible DNA licensing.
Q3. Can I reuse my ISR4000 DNA license when moving to Catalyst 8000?
Yes. Cisco Smart Licensing supports DNA license migration from ISR4000 or ASR1000 to Catalyst 8000 routers, preserving existing entitlements and subscription terms.
Q4. What is the difference between DNA Essentials and DNA Advantage?
DNA Essentials provides standard routing and automation, while DNA Advantage includes SD-WAN, segmentation, and advanced analytics. For controller-managed networks, DNA Advantage is required.
Q5. Do I need the HSEC license after replacing my ISR router?
If your encrypted (IPsec or SD-WAN) traffic exceeds 250 Mbps, an HSEC license is required on Catalyst 8000 routers to unlock full encryption throughput and remain compliant.
Q6. Will my network stop working if the DNA subscription expires?
No. The Network Stack license on Catalyst 8000 is perpetual, so routing continues even after DNA subscription expiry. However, controller functions (vManage, DNA Center) will be disabled until renewal.


