Your cart is currently empty!
If you open a networking textbook from ten years ago, an example of WAN (Wide Area Network) might list technologies like Frame Relay or ATM.
Ignore that advice. In 2025, those technologies are dead.
For modern network engineers and IT managers, a Wide Area Network is the lifeline that connects branches to data centers, and users to the Cloud. It is no longer just about “connecting cables”; it is about intelligence, security, and application performance.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore 7 real-world wide area network examples that are actually used in enterprise environments today. From the rock-solid reliability of MPLS to the flexibility of Cisco SD-WAN, we will breakdown which architecture fits your business.
Quick Summary: The 7 Types of WAN
- MPLS: Private, guaranteed performance for mission-critical voice/video.
- SD-WAN: The modern standard; bonding multiple links for efficiency.
- Internet VPN: Low-cost, encrypted connectivity for small sites.
- Metro Ethernet: High-speed fiber bridging buildings in the same city.
- 4G/5G Wireless WAN: Instant connectivity and failover.
- Hybrid WAN: The best of both worlds (MPLS + Internet).
- Cloud WAN: Direct private links to AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)
When asking for a traditional enterprise example of WAN, MPLS is the answer. Unlike the public internet, MPLS is a private network built by a Service Provider. It functions like a dedicated highway lane just for your company’s data.
- How it works: Data packets are assigned “labels.” Routers make forwarding decisions based on these labels rather than complex IP lookups.
- Best For: Real-time applications like VoIP phones (Cisco IP Phones) and Video Conferencing where even a millisecond of lag is unacceptable.
- The Downside: It is expensive (cost per Mbps) and takes weeks or months to provision.
Cisco Hardware Match: Traditionally Cisco ISR 4000 Series, now upgrading to Cisco Catalyst 8300 Series Edge Platforms.
SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN)
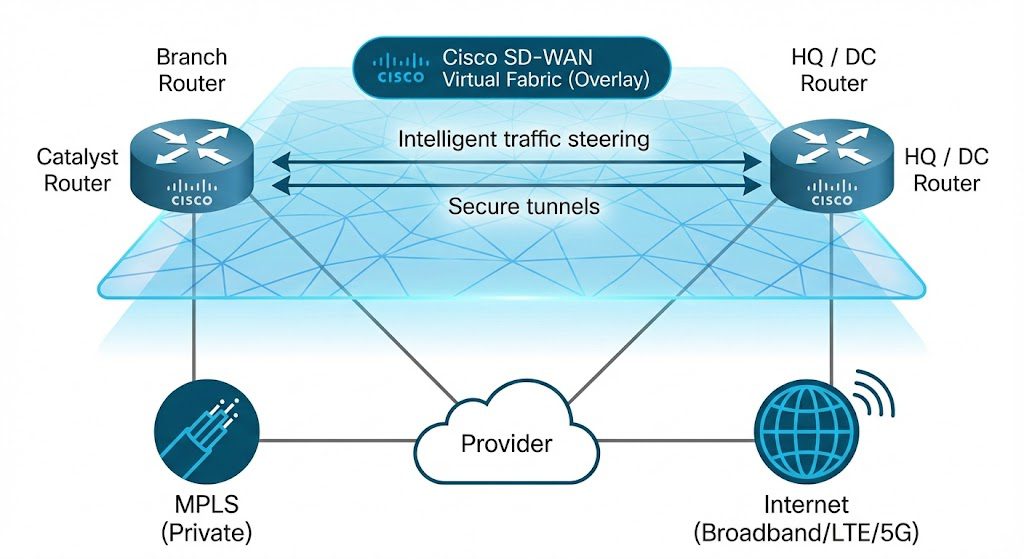
This is the most critical wide area network example for 2025. SD-WAN is not a connection type itself; it is an intelligent software layer that sits on top of your physical connections.
- How it works: Imagine you have two connections: an expensive MPLS line and a cheap broadband cable. SD-WAN analyzes traffic in real-time. It sends critical SAP data over MPLS and YouTube traffic over broadband. If one line fails, it instantly reroutes traffic without dropping the call.
- Real-World Scenario: A retail chain with 500 stores uses SD-WAN to reduce MPLS costs by 50% while increasing bandwidth using local internet.
- Why it wins: It provides “Application Awareness.” The network knows what the traffic is, not just where it is going.
Cisco Solution: Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN (Viptela) for enterprise core, or Cisco Meraki MX for lean IT teams.
Site-to-Site VPN (IPsec)
For small businesses or home offices, paying for a private line is impossible. The solution is using the public Internet as a wide area network example.
- How it works: Detailed encryption (IPsec) creates a secure “tunnel” through the public internet. To the user, it looks like a private connection.
- Best For: Small branch offices, teleworkers, or temporary sites.
- The Risk: You are at the mercy of public internet congestion. There is no QoS (Quality of Service) guarantee.
Metro Ethernet (Metro-E)
Metro Ethernet is a unique example of WAN that behaves like a LAN. If your company has two office buildings in the same city (e.g., New York City or London), ISPs can provide a dark fiber connection between them.
- Speed: Extremely fast (1Gbps, 10Gbps, or even 100Gbps).
- Latency: Near zero.
- Use Case: Data Center mirroring, University campuses, or Hospital systems sharing large imaging files.
Wireless WAN (4G LTE / 5G)
Cellular is no longer just for mobile phones. With the speed of 5G, wireless is now a legitimate primary or backup WAN transport.
- Real-World Scenario (Failover): A construction crew cuts the fiber cable outside your office. Normally, your business would go offline. With a Cisco Cellular Gateway, your router instantly switches to 5G, and no one notices the outage.
- Real-World Scenario (Pop-up): A mobile healthcare clinic needs internet immediately. They cannot wait for fiber installation.
Cisco Hardware Match: Cisco Catalyst Cellular Gateways (MG Series) or ISR routers with NIM-LTE modules.
Hybrid WAN
Most large enterprises do not choose just one. They choose a Hybrid WAN.
- Definition: A Hybrid WAN uses at least two different types of transport technologies—usually MPLS (for reliability) and Internet (for bandwidth).
- Why use it? It offers the security of a private network for critical data, with the low cost of the internet for bulk data. This is the foundation of most SD-WAN deployments.
Cloud WAN (Direct Connect / ExpressRoute)
Modern WANs don’t just connect offices; they connect to the Cloud. Services like AWS Direct Connect or Azure ExpressRoute are specialized wide area network examples. They are private fiber links from your data center directly into the cloud provider’s network, bypassing the public internet for security and speed.
Comparison: Which WAN Architecture is Right for You?
|
Feature |
MPLS |
SD-WAN / Hybrid |
Internet VPN |
5G Wireless |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cost |
$$$$(High) |
$$ (Medium) |
$ (Low) |
$$ (Variable) |
|
Reliability |
99.999% SLA |
High (Active/Active) |
Variable |
Good |
|
Deployment Time |
Weeks/Months |
Days |
Hours |
Instant |
|
Security |
Private (High) |
Encrypted (High) |
Encrypted (High) |
Encrypted |
|
Best For |
Voice/Video HQ |
Enterprise Branches |
Small/Home Office |
Backup/Mobile |
Cisco Hardware Matrix: Building Your WAN
As a Cisco Solutions provider, we don’t just explain the theory; we supply the hardware. Here is the standard mapping for 2025:
- For the Core / Data Center (The Powerhouse):
- Product: [Cisco Catalyst 8500 Series Edge Platforms]
- Role: High-performance 40G/100G aggregation for MPLS and SD-WAN headends.
- For the Branch Office (The Workhorse):
- Product: [Cisco Catalyst 8300 / 8200 Series]
- Role: The successor to the ISR 4000. Perfect for SD-WAN, security, and edge computing.
- For Simple / Cloud-Managed IT:
- Product: [Cisco Meraki MX Series]
- Role: “Plug and Play” SD-WAN. Ideal for retail, hospitality, and lean IT teams.
FAQ: Common Questions about WAN Types
Q: What is the most common example of WAN?
Historically, MPLS was the most common commercial example. However, in 2025, SD-WAN (utilizing a mix of broadband and MPLS) has become the standard for modern enterprises due to its cost-efficiency.
Q: Is Wi-Fi a wide area network example?
No. Wi-Fi is a LAN (Local Area Network) technology. A WAN (like Fiber or 5G) connects that Wi-Fi network to the internet or other offices.
Q: Can I use 5G as my only WAN connection?
Yes. For small branches or pop-up stores (like kiosks), 5G is a perfectly valid example of WAN connectivity, provided you use enterprise-grade hardware like Cisco Catalyst Cellular Gateways.
Summary: Upgrade Your Network Today
The definition of a Wide Area Network has evolved. It is no longer just about connecting Point A to Point B; it is about choosing the right mix of Performance, Cost, and Agility.
Whether you need the heavy-duty power of the Cisco Catalyst 8000 or the simplicity of Meraki SD-WAN, understanding these examples is the first step.