Your cart is currently empty!
RJ45 (Registered Jack 45) is a connector interface widely used for Ethernet networking. It is typically paired with twisted-pair network cables to connect computers, switches, routers, and other network devices.
An RJ45 plug (often called an RJ45 “crystal head”) is usually made of a plastic shell with metal contacts. A standard RJ45 plug has 8 metal pins corresponding to 8 conductors in the cable. Clean, reliable contact between pins and conductors is critical to signal quality.
Twisted Pair Cables with RJ45
Twisted pairs come in UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) and STP (Shielded Twisted Pair). UTP is common for general Ethernet links, while STP is used where EMI must be mitigated.
Inside the cable, the 8 conductors follow color codes commonly used as references during installation: white-orange, orange, white-green, blue, white-blue, green, white-brown, brown.
RJ45 Wiring Standards
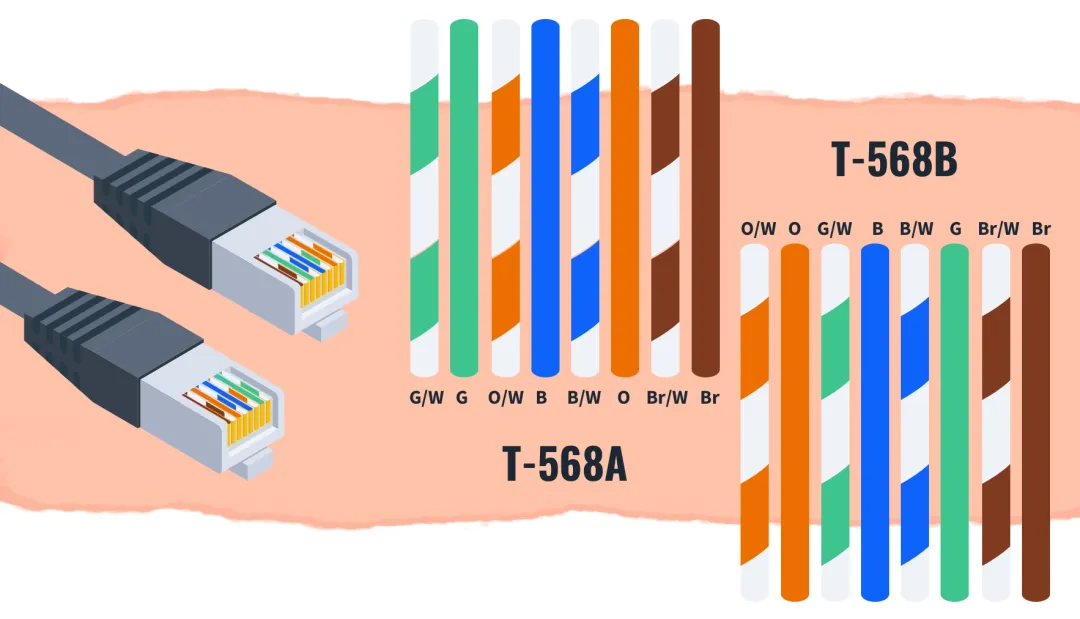
Two common RJ45 pinout standards are TIA/EIA-568A and TIA/EIA-568B. They define the color coding and the order of conductors in the RJ45 plug. Although similar, choosing the correct standard matters in specific applications and for compatibility.
T568A Wiring Standard
In the 568A standard, the conductor order is:
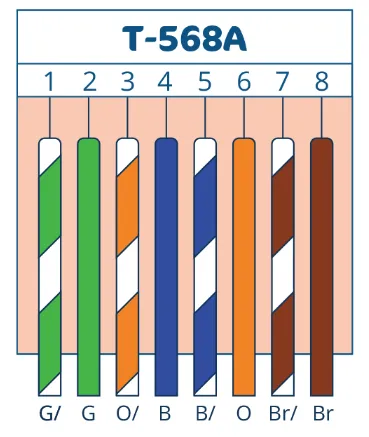
- White-Green
- Green
- White-Orange
- Blue
- White-Blue
- Orange
- White-Brown
- Brown
T568B Wiring Standard
In the 568B standard, the conductor order is:
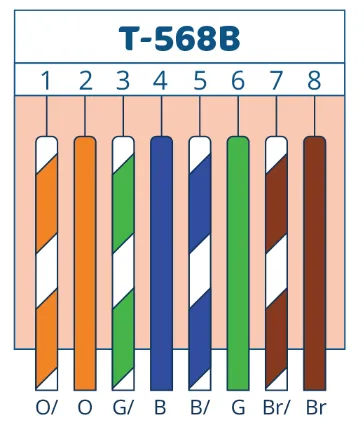
- White-Orange
- Orange
- White-Green
- Blue
- White-Blue
- Green
- White-Brown
- Brown
T568A vs T568B: Differences and How to Choose
The most obvious difference is the color pair used on pins 1 and 2.
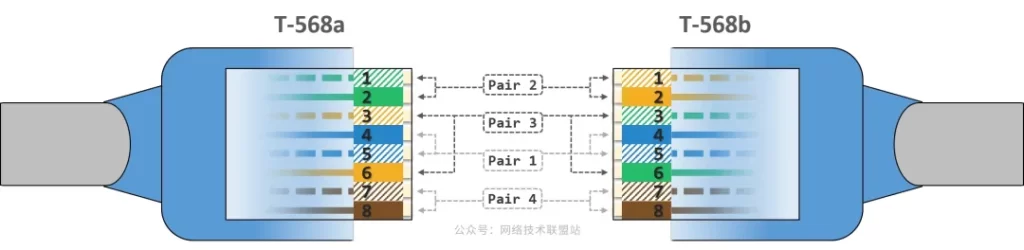
- 568A places the white-green/green pair on pins 1 and 2.
- 568B places the white-orange/orange pair on pins 1 and 2.
Other positions are essentially the same pattern, but the overall arrangement dictates usage scenarios.
Historically, 568A was the earliest wiring standard, first used in government and certain specialized sectors. 568B gained popularity later and gradually became the mainstream choice in commercial and residential cabling. Because of these historical and application differences, selecting the appropriate standard is essential for compatibility and performance.
In practice, depending on the connection, you may make straight-through cables or crossover cables:
- Straight-through cable: both ends use the same standard (e.g., 568A-568A or 568B-568B).
- Crossover cable: the two ends use different standards (e.g., 568A-568B), traditionally for connecting two like devices (e.g., PC-to-PC).
How to Make an RJ45 Ethernet Cable
Tools and materials:
- RJ45 plugs
- Twisted-pair cable (Cat5e, Cat6, etc.)
- Crimping tool
- Wire stripper
- Cable tester
Step 1: Strip and Arrange
- Use the stripper to remove the outer jacket and expose the 8 conductors.
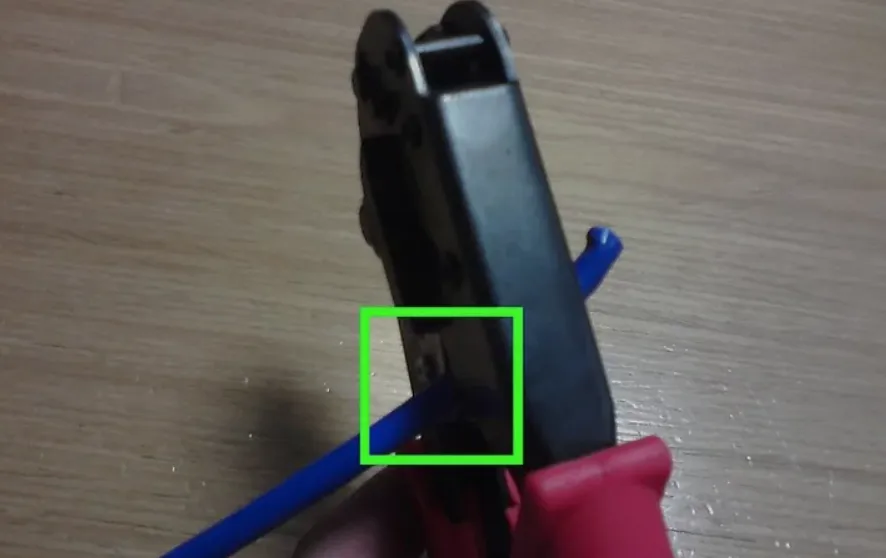

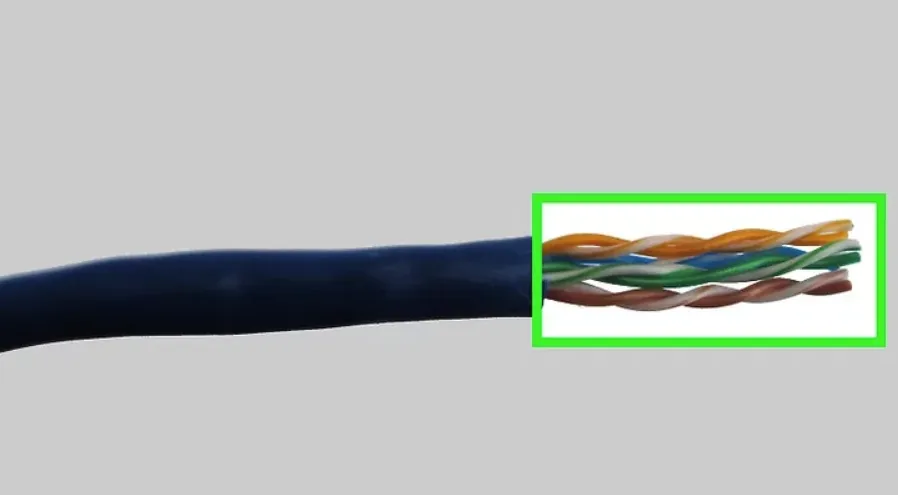
- Arrange the 8 wires according to your chosen standard (568A or 568B).
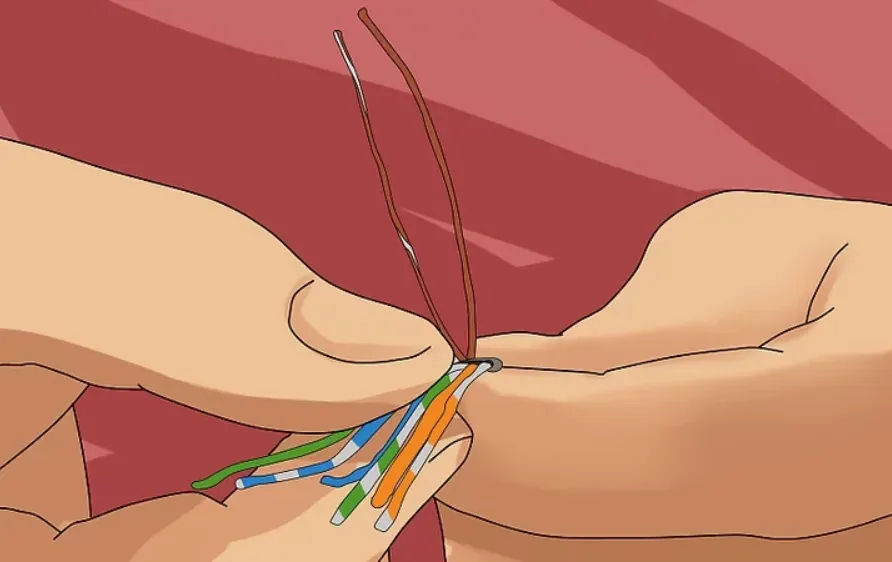
- Trim the ends evenly so they fit neatly into the plug.
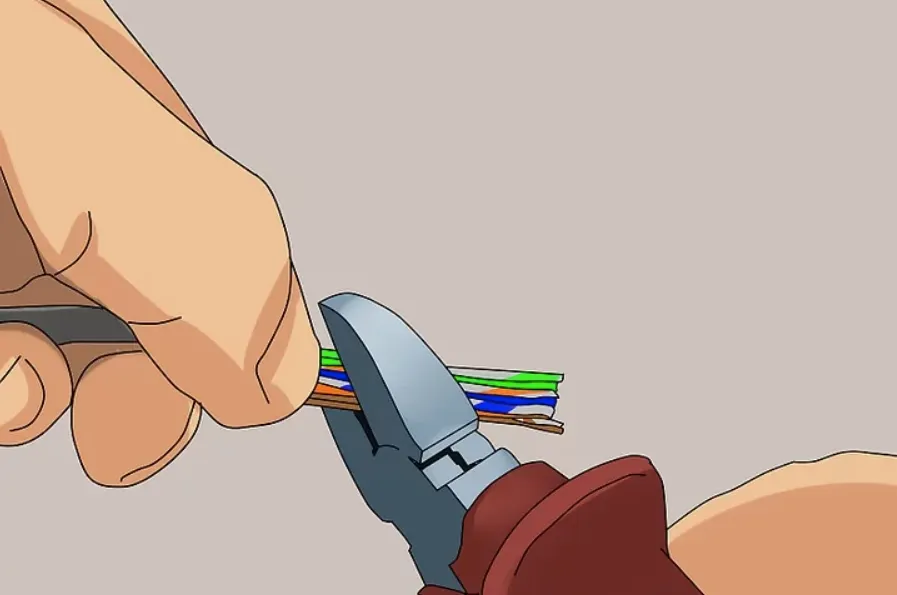

Step 2: Insert the RJ45 Plug
Insert the aligned conductors into the RJ45 plug, ensuring each wire slides fully into its correct slot beneath the metal contacts.
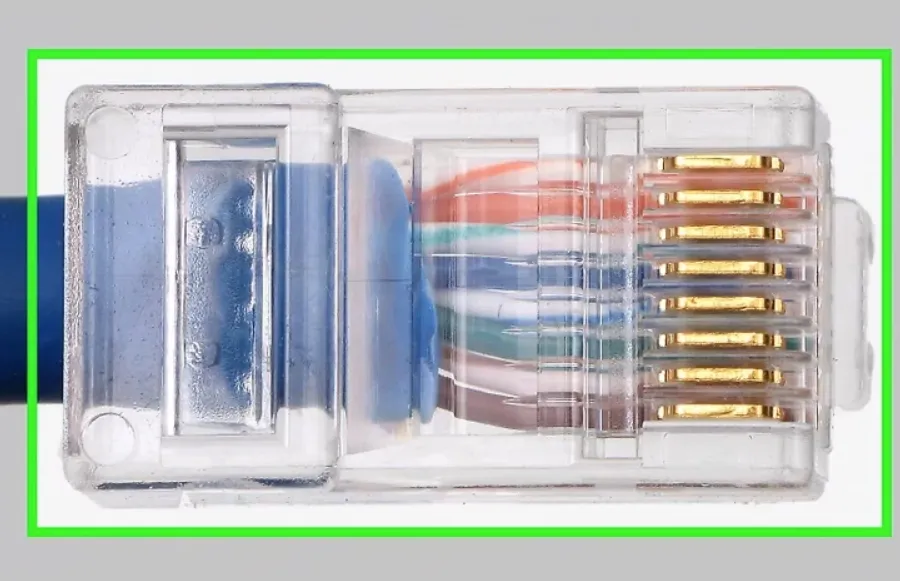
Step 3: Crimp and Secure
Use the crimping tool to press the contacts firmly into the conductors. Ensure the connection is tight and not easily loosened.
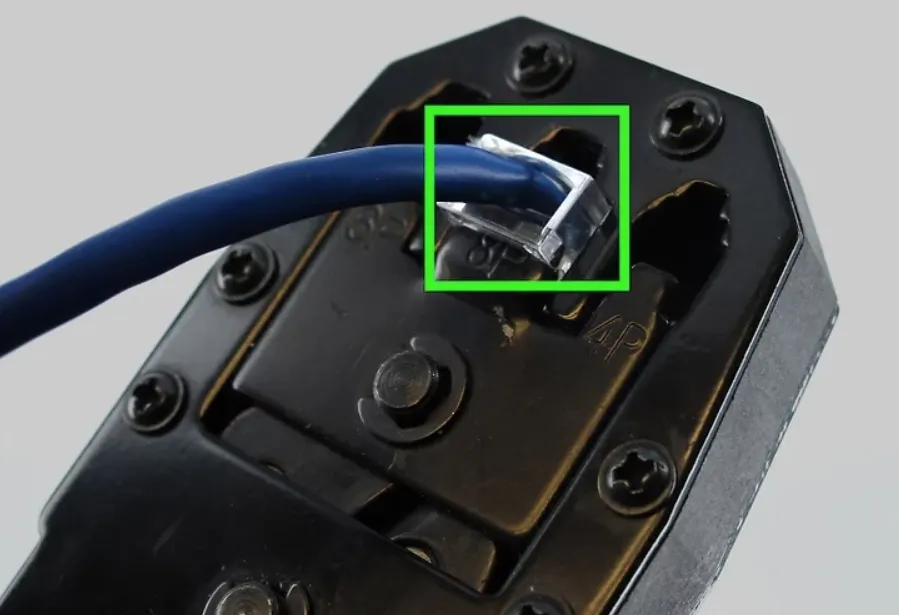
Step 4: Test the Cable
Use a cable tester to verify pin-to-pin continuity and detect any shorts or opens, confirming that every conductor matches its intended pin.
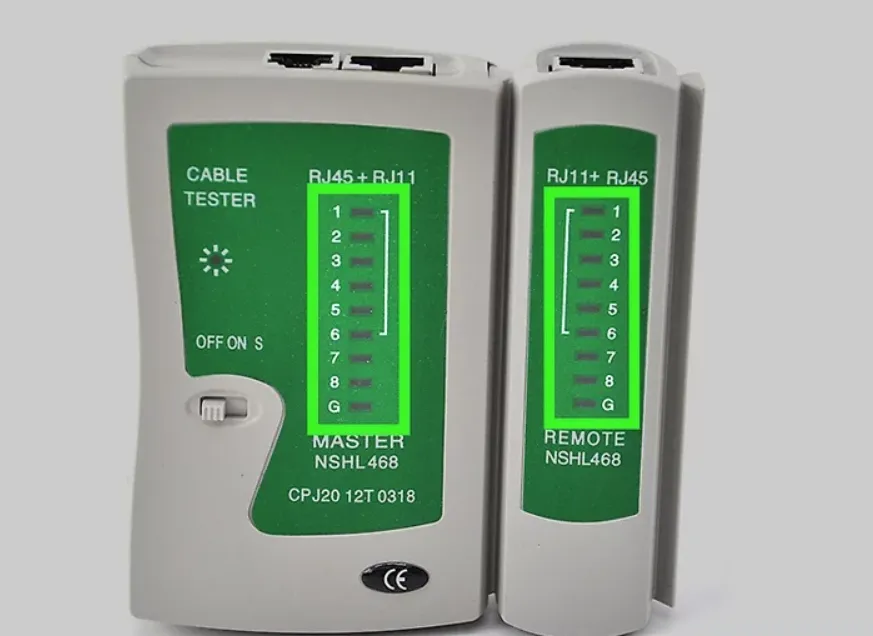


FAQs (T568A vs T568B)
-
What’s the difference between T568A and T568B RJ45 pinouts?
Both are TIA/EIA standards with the same electrical performance; the only change is the pair on pins 1–2: 568A uses white-green/green, 568B uses white-orange/orange.
-
Which is better—T568A or T568B?
Neither is inherently better. Pick one standard and use it consistently across your site; 568B is common in commercial installs, while 568A appears in some residential/government projects.
-
When do I use straight-through vs crossover wiring?
Use straight-through (568A–568A or 568B–568B) for most links. Crossover (568A–568B) is for legacy device-to-device connections; many modern NICs support auto-MDI/MDIX, making crossover rarely necessary.
-
Can I put T568A on one end and T568B on the other?
Yes, but that creates a crossover cable. Do it only if you specifically need a crossover; otherwise keep both ends the same standard.
-
Does T568A vs T568B affect Cat5e/Cat6 performance, PoE, or 10G?
No. Performance depends on cable category (Cat5e/Cat6/Cat6a), install quality, and length—not on A vs B. PoE works with either standard if the terminations are done correctly.
-
How can I verify the RJ45 pinout and wiring order?
Use a cable tester to check pin-to-pin continuity and pair mapping, confirm clip orientation, follow the color code exactly, and re-crimp any failing pairs.
Choosing cable for home vs enterprise? Start with the Cat5 vs Cat5e vs Cat6 vs Cat6a: Ethernet Cable Comparison 2025





