Your cart is currently empty!
What is Cat6? Cat6 (Category 6) is a high-performance twisted-pair Ethernet cable standard defined by EIA/TIA. It supports up to 250 MHz bandwidth and up to 10 Gbps under suitable conditions, offering lower crosstalk and better interference resistance for home, enterprise, and data-center cabling.
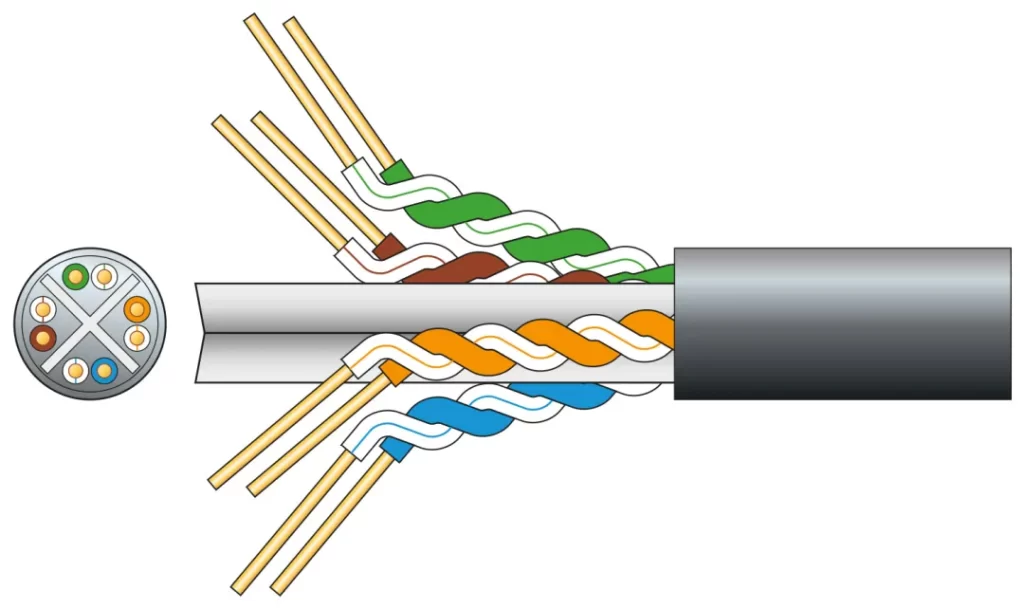
Cat6 Cable Structure
A Cat6 cable typically contains four twisted pairs, each pair consisting of insulated copper conductors. The pairs are precisely insulated and twisted to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). The outer jacket commonly uses PVC or LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) materials to ensure protection and durability.
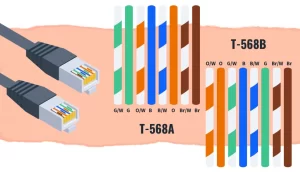
Cat6 Termination and RJ45 Connections
Cat6 can be connected to network devices in several ways; the most common is the RJ45 connector. RJ45 allows Cat6 to plug into computers, routers, switches, and other network equipment to establish connectivity. Depending on cabling needs and topology, Cat6 can also be terminated with various modules, keystone jacks, or patch panels to connect different types of devices.
Use T568A or T568B consistently at both ends to avoid split pairs and performance loss.
Cat6 Performance: Bandwidth, Speed, Crosstalk & EMI
Cat6 is favored for its robust performance characteristics across diverse network environments and use cases.
High Bandwidth
Cat6 provides up to 250 MHz of bandwidth, enabling greater data throughput—ideal for high-speed networks.
Up to 10 Gbps Data Rate
In theory, Cat6 supports up to 10 Gbps (10 Gigabit per second) over appropriate distances and conditions, making it suitable for large file transfers, video streaming, and other high-bandwidth applications.
Low Attenuation and Crosstalk
Cat6’s construction reduces signal attenuation and crosstalk, helping data travel with higher quality and stability while minimizing errors and packet loss.
Interference Resistance
With tighter twists and—on shielded variants—foil/braid screens, Cat6 better withstands external interference, suiting noisy industrial sites or dense office buildings.
Cat6 Use Cases
- Enterprise Networks
Cat6 is common in enterprise LANs, offering higher data rates and more bandwidth for office buildings, campus networks, and data centers. It supports multiple applications such as file sharing, video conferencing, and cloud services. In enterprise networks, shielded Cat6 (STP) is generally preferred. - Data Centers
Data centers demand high-speed, high-bandwidth connectivity for large-scale storage and compute. Cat6 delivers excellent performance for linking servers, storage, and network devices. Data centers typically select shielded Cat6 (STP). - HD Video Surveillance
Video surveillance systems require high bandwidth to carry HD streams. Cat6 meets these needs, making it a top choice between cameras and monitoring systems. HD surveillance often uses unshielded Cat6 (UTP). - High-Performance Computing (HPC)
HPC environments need massive data transfers and fast networking for complex scientific workloads. Cat6 supports rapid inter-node communications in HPC clusters. - Home Networks
Cat6 is increasingly the go-to for homes. It supports multiple devices simultaneously for streaming, online gaming, and smart-home gear. Home networks commonly choose unshielded Cat6 (UTP). - Power over Ethernet (PoE) Applications
Cat6 excels with PoE, which delivers power over the same network cable to IP cameras, VoIP phones, Wi-Fi APs, and more. Cat6 provides stable power delivery with less loss. For PoE, select CMR or CMP-rated Cat6 cable as appropriate for riser or plenum spaces.
Choosing cable for home vs enterprise? Start with the Cat5 vs Cat5e vs Cat6 vs Cat6a: Ethernet Cable Comparison 2025
Verify 802.3af/at/bt class and headroom when sizing the PoE budget over Cat6.
UTP vs STP Cat6
The main difference between UTP Cat6 (unshielded) and STP Cat6 (shielded) lies in interference protection.
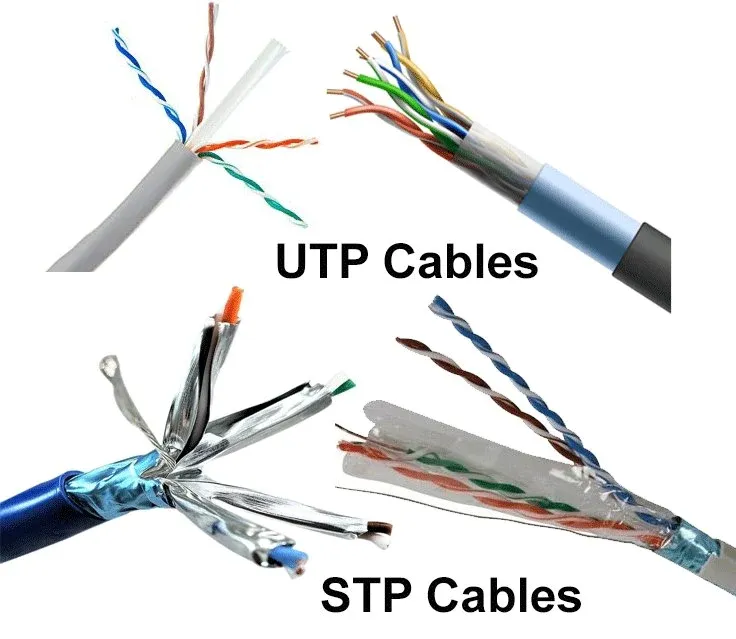
UTP Cat6 (Unshielded)
- Lower shielding: no additional foil/braid shield to block EMI.
- Typical use: home networks, enterprise interiors, small offices, and general indoor runs—e.g., from PCs to wall jacks or to switches.
STP Cat6 (Shielded)
- Stronger shielding: includes foil and/or braid to block EMI, offering superior performance in high-interference environments.
- Typical use: data centers, industrial sites, high-speed links (e.g., 10GbE), and some outdoor runs—anywhere higher signal integrity and reliability are needed.
If your environment has little EMI or only general performance needs, UTP Cat6 is often sufficient. For higher interference or 10GbE and above, STP Cat6 is the better choice.
Solid vs Stranded Cat6
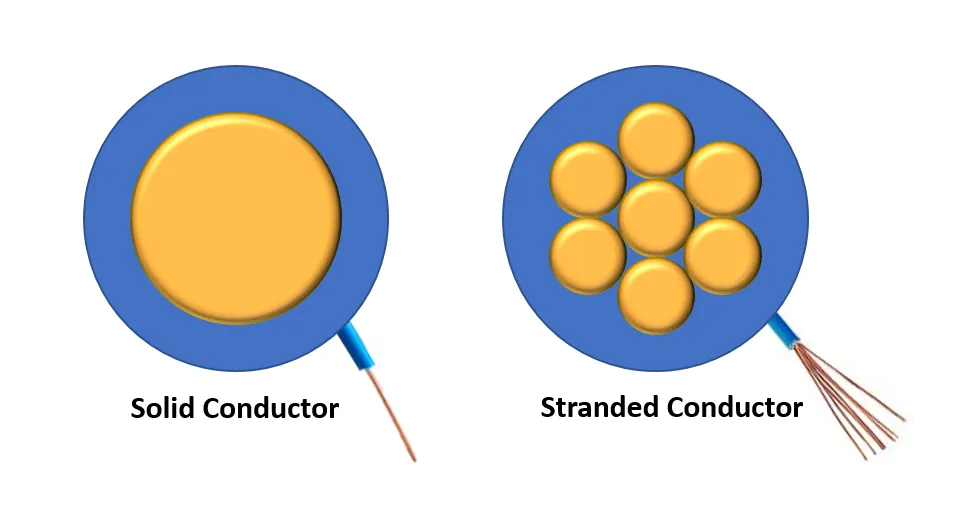
Solid Cable
- More durable: a single solid copper conductor per wire, ideal for permanent installations (in-wall, risers, long runs).
- Longer reach: typically supports longer distances due to lower signal loss.
- Lower attenuation: maintains signal quality for high-speed transmission.
Stranded Cable
- More flexible: multiple fine copper strands per wire, easy to bend and move—great for desks and patching.
- Shorter runs: better suited for short distances due to higher loss.
- Common for patch cords: used between NICs and wall plates, or between patch panels, hubs, and rack gear.
Use solid Cat6 for permanent links and longer distances; use stranded Cat6 for patch cords and short, flexible connections. Many cabling projects deploy solid for the backbone and stranded for the final device jumpers—choose based on requirements and budget.
Cat6 Installation & Maintenance Best Practices
Installation Requirements
- Cat6 performance depends on proper installation. Keep these best practices in mind:
- Proper Cable Routing: Keep runs as short and straight as possible and avoid excessive bends to reduce attenuation and interference.
- Quality Termination: Choose high-quality connectors to ensure stable, high-performance links. Cat6 typically uses RJ-45.
- Shielding and Grounding: Where needed, use shielded cable to minimize external interference, and ensure proper grounding of connectors and equipment to improve signal quality.
Maintenance and Testing
- After installation, regular maintenance and testing are key to sustained performance:
- Scheduled Maintenance Plan: Set a schedule to inspect connectors and cable condition, and remove dust or debris that may affect signal quality.
- Signal Quality Testing: Periodically test to verify performance—measure bandwidth, throughput, and interference using appropriate certification/test instruments.
FAQ
-
What is Cat6 used for?
High-speed Ethernet cabling for homes, offices, campuses, data centers, HD surveillance, and PoE devices.
-
Is Cat6 good for 10 Gbps?
Yes, Cat6 can support up to 10 Gbps at suitable distances/conditions; for longer 10G runs, consider Cat6a.
-
What’s the difference between Cat6 UTP and STP?
UTP has no extra shielding and fits general indoor runs; STP adds foil/braid for EMI-heavy or high-speed environments.
-
Solid vs stranded Cat6—which to choose?
Solid for permanent links/longer runs; stranded for flexible short patch cords.
-
Can Cat6 carry PoE?
Yes. Pick proper CMR/CMP-rated Cat6 and ensure total power budget matches PoE device needs.