Your cart is currently empty!
In modern industrial automation, rail transit, power systems, and smart factories, the installation method of industrial switches is as critical as their bandwidth, port density, redundancy, or protection rating. Choosing the right industrial switch installation method directly impacts heat dissipation, reliability, maintenance costs, and long-term system stability.
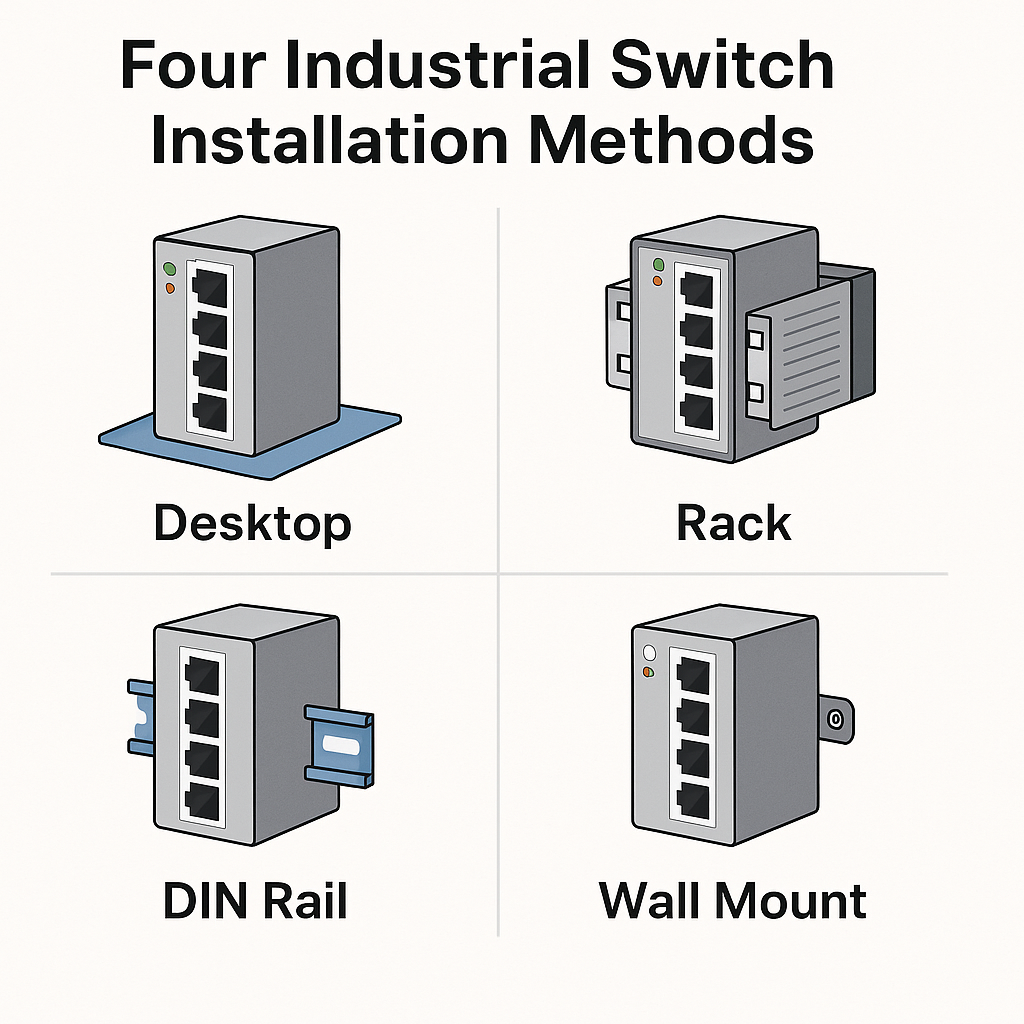
The choice of industrial switch installation methods directly impacts cooling, protection, maintenance convenience, overall network stability, and long-term operating costs. Different installation options are suited to different environments.
Here, we explore the four most common installation methods for industrial switches:
- Desktop installation of industrial switches
- Rack-mounted industrial switches
- DIN rail industrial switch installation
- Wall mount switch installation
Desktop Installation of Industrial Switches
Desktop installation is the most straightforward approach—placing the switch like a small box directly on a table, control panel surface, or equipment rack without extra fixtures.
Key Features
- Simple setup: No tools required, ready to use out of the box.
- High flexibility: Easy to move or reposition.
- Low cost: No need for racks, rails, or brackets.
Typical Scenarios
- Laboratory environments for temporary test networks.
- Small industrial projects with limited data points and devices.
- Emergency or temporary deployments at construction sites or field locations.
Considerations
- Heat dissipation: Leave ventilation space around the unit; avoid stacking.
- Protection level: Though rated IP30/IP40, desktop placement exposes devices to dust or moisture.
- Stability: Vulnerable to bumps or vibrations, not recommended for heavy-duty workshops.
Desktop installation is best for testing, small projects, or temporary industrial switch setups—often just a transitional solution.
Rack-Mounted Industrial Switches
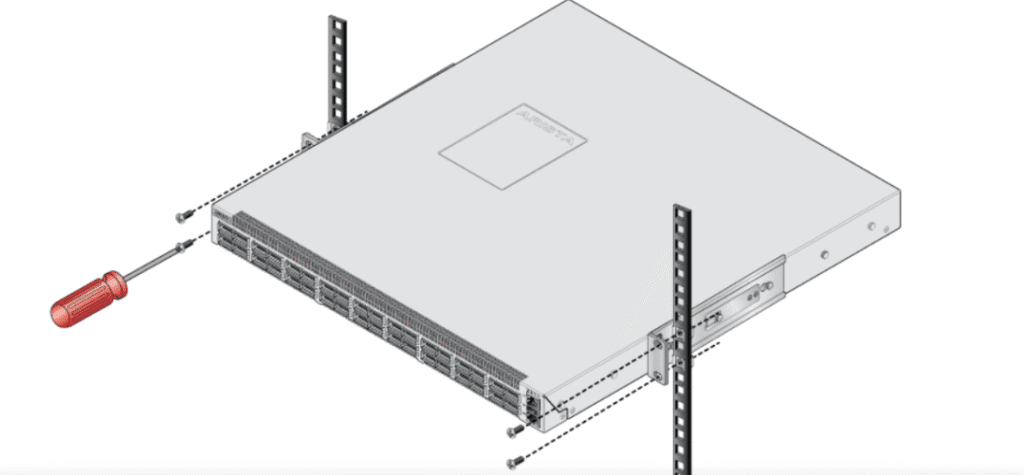
Rack mounting is the most common choice in enterprise and large-scale industrial settings. These switches follow the 19-inch rack standard and are secured inside cabinets with screws.
Key Features
- Standardized: 19-inch racks support switches, routers, firewalls, and more.
- Centralized management: Simplifies cabling and maintenance.
- Scalable: Multiple switches can be stacked into a network core.
- Effective cooling: Racks are usually equipped with fans or AC for stable operation.
Typical Scenarios
- Large factory data centers with numerous rack-mounted industrial switches.
- Rail transit control centers requiring reliable, scalable communications.
- Power dispatch rooms or communication equipment rooms with high-density deployments.
Considerations
- Space planning: Switches occupy 1U or 2U—plan rack space in advance.
- Cable management: Use cable trays and organizers to reduce clutter.
- Environmental protection: Ensure racks are dust-proof, moisture-resistant, with UPS backup.
- Maintenance cost: Requires professional installation and management.
Rack-mounted industrial switches are the gold standard for centralized, large-scale networks.
DIN Rail Industrial Switch Installation
DIN rail mounting is practically the default installation method for industrial switches. A DIN rail is an international standard metal track (typically 35 mm wide). The switch clips directly onto the rail.
Key Features
- Quick installation: Simply snap the switch onto the rail.
- Compact layout: Aligns neatly with PLCs, power supplies, and relays.
- Easy maintenance: Remove or replace units with minimal effort.
- Vibration resistant: Mounted inside cabinets for better stability than desktop setups.
Typical Scenarios
- Industrial automation control cabinets with PLCs and I/O modules.
- Power substations where compact cabinet space matters.
- Rail transit and energy sector systems requiring modular, scalable designs.
Considerations
- Space planning: Leave enough clearance for ventilation.
- Rail standards: Ensure compatibility—35 mm is most common.
- Cabinet design: Despite IP protection, dust and moisture control remains essential.
DIN rail industrial switch installation is the most efficient and widely adopted method in modern factories.
Wall Mount Switch Installation

When racks or rails are unavailable—or when space is extremely limited—wall mounting becomes the practical choice. Switches are fixed to walls or cabinet interiors using screws or hooks.
Key Features
- Space saving: No need for racks or table space.
- Flexible placement: Choose mounting height and position based on site needs.
- Easy cabling: Located near walls or cabinet edges for streamlined wiring.
Typical Scenarios
- Small control boxes with limited interior space.
- Rail transit vehicle equipment compartments.
- Compact outdoor distribution boxes where wall mount switch installation is more practical than DIN rail.
Considerations
- Secure fastening: Use proper screws/brackets to prevent loosening under vibration.
- Maintenance difficulty: Requires unscrewing, less convenient than DIN rail.
- Heat dissipation: Maintain clearance from other equipment.
Wall mount switch installation is a flexible alternative for small projects or special environments where space is restricted.
Comparison of Industrial Switch Installation Methods
Choosing an industrial switch installation method is about much more than just “fixing the device in place.” It reflects a holistic consideration of project scale, environmental conditions, and maintenance practices.
- Desktop installation: Simple and direct, best for small or temporary use.
- Rack-mounted installation: Standardized, reliable, ideal for large centralized setups.
- DIN rail installation: The most common choice in industrial sites, balancing efficiency and stability.
- Wall mount installation: A space-saving alternative for compact or special applications.
|
Installation Method |
Key Features |
Typical Scenarios |
Advantages |
Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Desktop |
Simple placement, no tools required |
Labs, small projects, temporary deployments |
Low cost, flexible, quick setup |
Poor stability in vibration environments, limited protection |
|
Rack-Mounted |
19-inch standard rack mounting |
Data centers, rail control rooms, power dispatch centers |
Centralized management, scalable, effective cooling |
Requires rack space, higher installation cost, less flexible |
|
DIN Rail |
35 mm rail clip-on installation |
Control cabinets, substations, automation systems |
Fast installation, compact, vibration resistant |
Needs rail compatibility, ventilation planning |
|
Wall-Mounted |
Screwed or hooked to wall/cabinet |
Small control boxes, outdoor enclosures, train compartments |
Space-saving, flexible placement, simple wiring |
Less convenient maintenance, must ensure secure fastening |
In practice, engineers often combine multiple industrial switch installation methods to optimize layouts for different devices.