Your cart is currently empty!
Short Answer :
EPON uses Ethernet-based transmission with symmetrical bandwidth and lower cost, while GPON uses TDM/GEM with higher downstream capacity, stronger QoS, and better multi-service support for large-scale FTTH deployments.
EPON vs GPON — Quick Comparison Table
|
Feature |
EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network) |
GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) |
|---|---|---|
|
Standard |
IEEE 802.3ah / 802.3av |
ITU-T G.984.x |
|
Protocol Type |
Ethernet |
TDM + GEM |
|
Downstream Rate |
1.25 Gbps / 10 Gbps |
2.5 Gbps |
|
Upstream Rate |
1.25 Gbps / 10 Gbps |
1.25 Gbps |
|
Symmetry |
Symmetric |
Asymmetric |
|
Split Ratio |
1:32 / 1:64 / 1:128 |
1:32 / 1:64 / 1:128 |
|
QoS |
Basic (VLAN-based) |
Advanced (voice, video, data) |
|
Management |
Simple OAM |
OMCI / advanced OAM |
|
Best Use Case |
Enterprise, campus, symmetrical needs |
FTTH, ISP, residential broadband |
|
Cost |
Lower |
Higher |
What Is EPON?
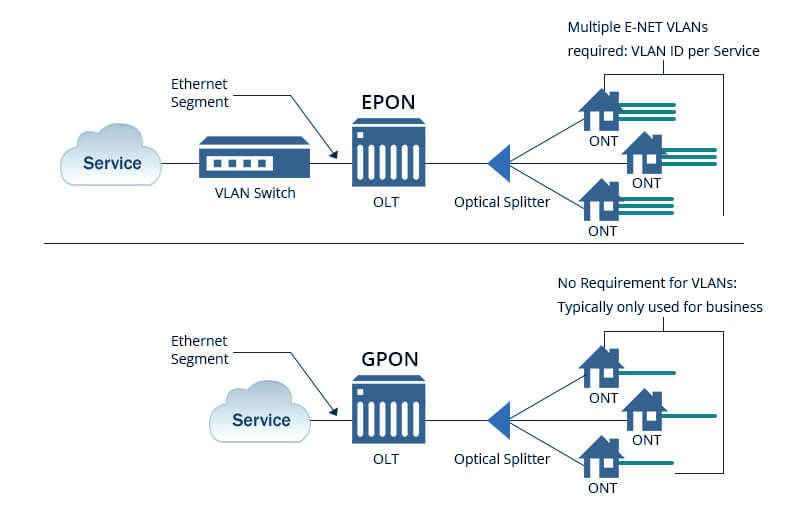
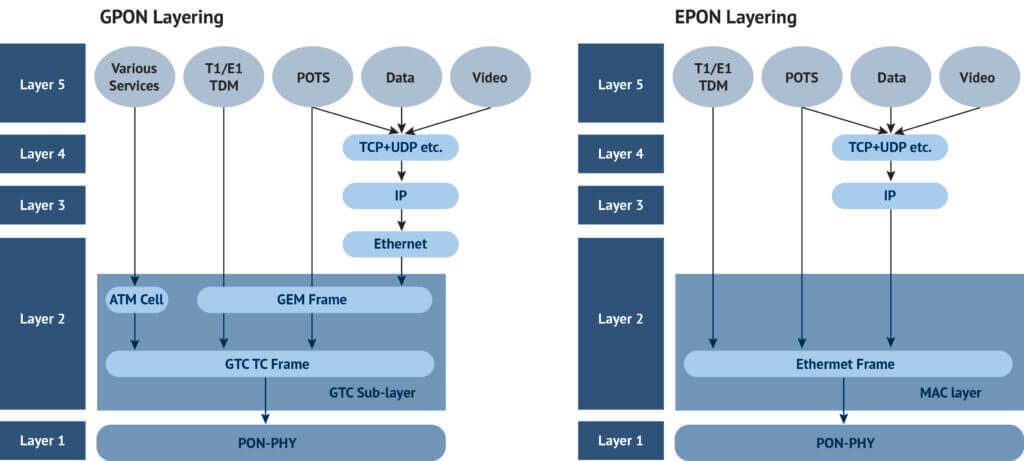
EPON stands for Ethernet Passive Optical Network. It uses standard Ethernet frames for data transmission, making it easy to integrate with existing Ethernet infrastructure.
EPON supports symmetrical upstream and downstream bandwidth and is available in both 1G EPON and 10G-EPON versions. Its architecture is simple, cost-effective, and widely used in enterprise and campus environments.
Key Characteristics of EPON
- Ethernet-native transmission
- Symmetric bandwidth
- Lower protocol overhead
- Simple deployment
- Ideal for enterprise or symmetrical traffic
Advantages of EPON
- Lower equipment cost
- High upstream performance
- Easy integration with Ethernet networks
Disadvantages of EPON
- Lower downstream performance for multi-user residential networks
- Basic QoS
- Less suitable for large-scale triple-play services
What Is GPON?
GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network. It uses GEM encapsulation and TDM scheduling to efficiently deliver multi-service traffic such as internet, IPTV, and VoIP.
GPON typically supports 2.5 Gbps downstream and 1.25 Gbps upstream, making it highly efficient for FTTH broadband deployments.
Key Characteristics of GPON
- High downstream capacity
- Optimized for multi-service networks
- Strong native QoS
- Widely used in residential broadband
Advantages of GPON
- Better support for IPTV, VoIP, and video services
- Strong QoS for stable performance
- Suitable for large-scale ISP deployments
- High split ratio options
Disadvantages of GPON
- Higher equipment cost
- Asymmetric bandwidth (upload limited)
- More complex deployment and management
EPON vs GPON — Detailed Specification Comparison
|
Parameter |
EPON |
GPON |
|---|---|---|
|
Standard |
IEEE 802.3ah / 802.3av |
ITU-T G.984 |
|
Encapsulation |
Ethernet frames |
GEM encapsulation |
|
Downstream |
1.25G / 10G |
2.5G |
|
Upstream |
1.25G / 10G |
1.25G |
|
Latency |
Lower (Ethernet-based) |
Low, optimized for multi-service |
|
Split Ratio |
Up to 1:128 |
Up to 1:128 |
|
QoS |
VLAN-based |
Hierarchical QoS |
|
Service Support |
Data primarily |
Data, IPTV, VoIP |
|
OAM |
Ethernet OAM |
OMCI / PLOAM |
|
Cost |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Deployment Complexity |
Low |
Medium / high |
|
Typical Use |
Enterprise / campus |
FTTH / ISP |
EPON vs GPON — Pros & Cons Summary
|
Technology |
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|---|
|
EPON |
Low cost, symmetric bandwidth, simple |
Lower downstream, basic QoS |
|
GPON |
High downstream, strong QoS, multi-service |
Higher cost, asymmetric bandwidth |
Best Use Cases for EPON and GPON
EPON Is Best For:
- Enterprise networks
- Campus networks
- Industrial and surveillance systems
- Upload-heavy workloads
- Cost-sensitive projects
- Ethernet-based infrastructure
GPON Is Best For:
- FTTH (Fiber-to-the-Home)
- ISPs and telecom operators
- IPTV, VoIP, triple-play
- High-density residential networks
- Heavy downstream traffic
- Multi-tenant buildings
Which Is Better: EPON or GPON?
Choose EPON if:
- You need symmetrical bandwidth
- You have a cost-sensitive deployment
- Your environment is enterprise/campus rather than residential
- You need strong upload performance
- You want simple Ethernet-native integration
Choose GPON if:
- You are building FTTH broadband for many users
- You need stable IPTV/VoIP/video services
- You require downstream-heavy throughput
- You need better QoS and service management
- You plan long-term residential expansion
2025 Trends — EPON vs GPON Evolution
- 10G-EPON adoption increasing, especially for enterprise upgrades
- XG-PON / XGS-PON expanding in global FTTH deployments
- Hybrid ODN designs allow GPON + XGS-PON coexistence
- Optical components becoming cheaper, narrowing cost differences
- Greater emphasis on QoS and multi-service, favoring GPON in residential markets
- Symmetric 10G needs rising in business environments, favoring 10G-EPON
EPON vs GPON — FAQ
-
Is EPON faster than GPON?
EPON can be faster in uploads due to symmetry, but GPON has higher downstream performance.
-
Which technology is cheaper?
EPON is generally cheaper to deploy and maintain.
-
Which is better for home broadband?
GPON, because it supports IPTV, VoIP, and high downstream bandwidth.
-
Is EPON suitable for triple-play services?
Yes, but GPON offers stronger native support and QoS.
-
Can EPON and GPON run on the same ODN?
Yes. With proper wavelength planning, they can share the same splitter infrastructure.
-
Is 10G-EPON an upgrade path?
Yes. 10G-EPON is ideal for enterprise environments and symmetrical high-bandwidth needs.
Conclusion
EPON and GPON both deliver high-performance fiber access, but each fits different needs.
- EPON is cost-effective, symmetric, and ideal for enterprise or industrial use.
- GPON offers superior downstream capacity, multi-service support, and scalability for FTTH.
Choosing the right technology depends on your service type, budget, bandwidth patterns, and long-term growth plans.





